What is a DMARC record?
A DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) record describes a policy that email recipients (like Gmail, for example) should use to handle security for emails from your domain.
It is stored as one of your domain’s DNS Records.
DMARC works with SPF and DKIM records to help determine whether an email that appears to have been sent from your domain is legitimate or not. Specifically the DMARC policy determines what to do with emails that fail those SPF and DKIM checks.
Where can I add the DMARC record?
The DMARC record can be added by following these steps:
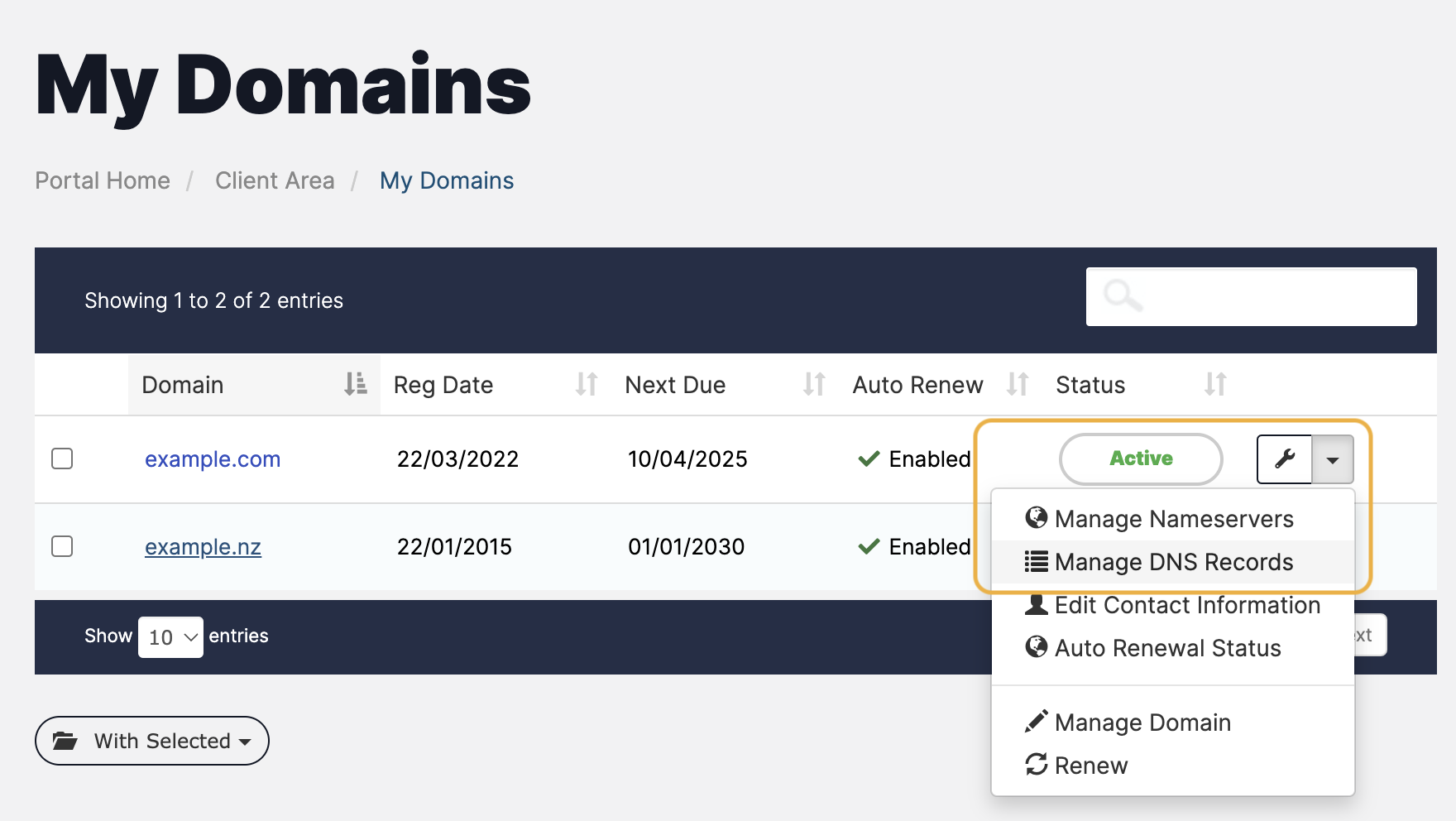
- In the MyHost client area, select Domains > My Domains. You will see a list of all your domains.
- Next to the domain that your emails are sent from, click the drop-down arrow.
- Select Manage DNS Records to open the domain’s DNS Manager (this can take a bit to load on larger DNS Zones). Under the list of current DNS records, you’ll see a set of empty fields where you can create a new record.
- Enter the Host Name
_dmarc. - Leave the default TTL.
- Select a Type of
TXT. - In the Value textbox, enter the DMARC record (see “What should my DMARC record look like?” below).
- Click Save Changes.
The new record will take some time to propagate.
What should my DMARC record look like?
If you are a small-to-medium business that doesn’t send a lot of emails (i.e. less than 5000 a day), then you should be OK with a record like this (replace example.com with your email domain):
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc@example.com
To break this down:
v=DMARC1- This is the version of DMARC this record is implemented for. For now only DMARC1 is valid.p=none- This is where you specify one of the three DMARC policies ("none", "quarantine", or "reject") to apply. The none policy still runs the SPF/DKIM checks on your emails, and they are all still delivered to their intended recipient. The results are merely attached to the headers for the receiving mail server to handle (in Gmail’s case it gets bounced back, while other services would add a ***SPAM*** tag for example).rua=mailto:dmarc@example.comsets the address that your DMARC reports will be sent to. Make sure you replaceexample.comwith your own domain, and that you enter a valid email address.
